Designing an Intelligent IVR for Banking Services with Kore.ai
Senior Product Conversational Designer (My Role)
Led IVR conversation design strategy
Designed user experience and interaction flows
Managed bot personality and tone development
Coordinated between technical and business teams
Conducted User Research, Design process and Review with stakeholders
Supervised conversation testing and optimization
In today’s fast-paced digital world, banking customers demand quick, efficient, and seamless access to their financial information and services. Traditional Interactive Voice Response (IVR) systems often fall short, leading to frustrating customer experiences. As a seasoned UX/UI Conversational Designer with over five years of experience in crafting seamless and scalable solutions , I was tasked with creating an intelligent IVR using Kore.ai to address these pain points. This case study outlines the human-centered design process I followed, from research to deployment, and how the solution transformed the banking experience for customers.
The Solution Journey
Step 1: Research – Understanding the Problem
Objective
To identify the pain points of banking customers when interacting with traditional IVR systems and understand their daily banking needs.
Methods
Customer Interviews: Conducted interviews with 50 banking customers to understand their frustrations with existing IVR systems.
Competitive Analysis: Analyzed IVR systems of leading banks to identify gaps and opportunities.
Data Analysis: Reviewed call center logs to identify common customer queries and pain points.
Key Findings
Customers found traditional IVRs to be rigid and time-consuming.
Common tasks like checking account balances and opening new accounts were frequently requested but poorly handled by IVRs.
Customers preferred self-service options over speaking to a live agent for simple tasks.
Visual: Customer Pain Points
Step 2: Ideation – Defining the Solution
Objective
To design an intelligent IVR that simplifies daily banking tasks and provides a personalized, conversational experience.
Approach
Persona Development: Created customer personas to represent different user segments (e.g., tech-savvy millennials, older adults unfamiliar with digital banking).
User Journeys: Mapped out user journeys for key tasks like checking account balances and opening new accounts.
Brainstorming Sessions: Collaborated with stakeholders to generate ideas for improving the IVR experience.
Key Features Proposed
Natural Language Understanding (NLU): Enable the IVR to understand and respond to customer queries in natural language.
Personalization: Use customer data to provide personalized responses (e.g., greeting customers by name).
Seamless Handoff to Live Agents: Allow the IVR to transfer customers to live agents when necessary.
Multi-Channel Integration: Ensure the IVR works seamlessly with other channels like mobile apps and websites.
Visual: User Journey Map
Step 3: Design – Crafting the Conversational Flow
Objective
To create a conversational flow that feels natural, intuitive, and efficient.
Tools Used
Kore.ai Platform: Leveraged Kore.ai’s NLU capabilities to design the conversational flow.
Prototyping Tools: Used tools like Figma and Miro to visualize the flow and gather feedback.
Key Design Decisions
Simple Menu Structure: Reduced the number of menu options to avoid overwhelming users.
Contextual Responses: Designed the IVR to remember context (e.g., if a customer asks about their account balance, the IVR can follow up with related questions).
Error Handling: Incorporated fallback responses to guide users when the IVR doesn’t understand a query.
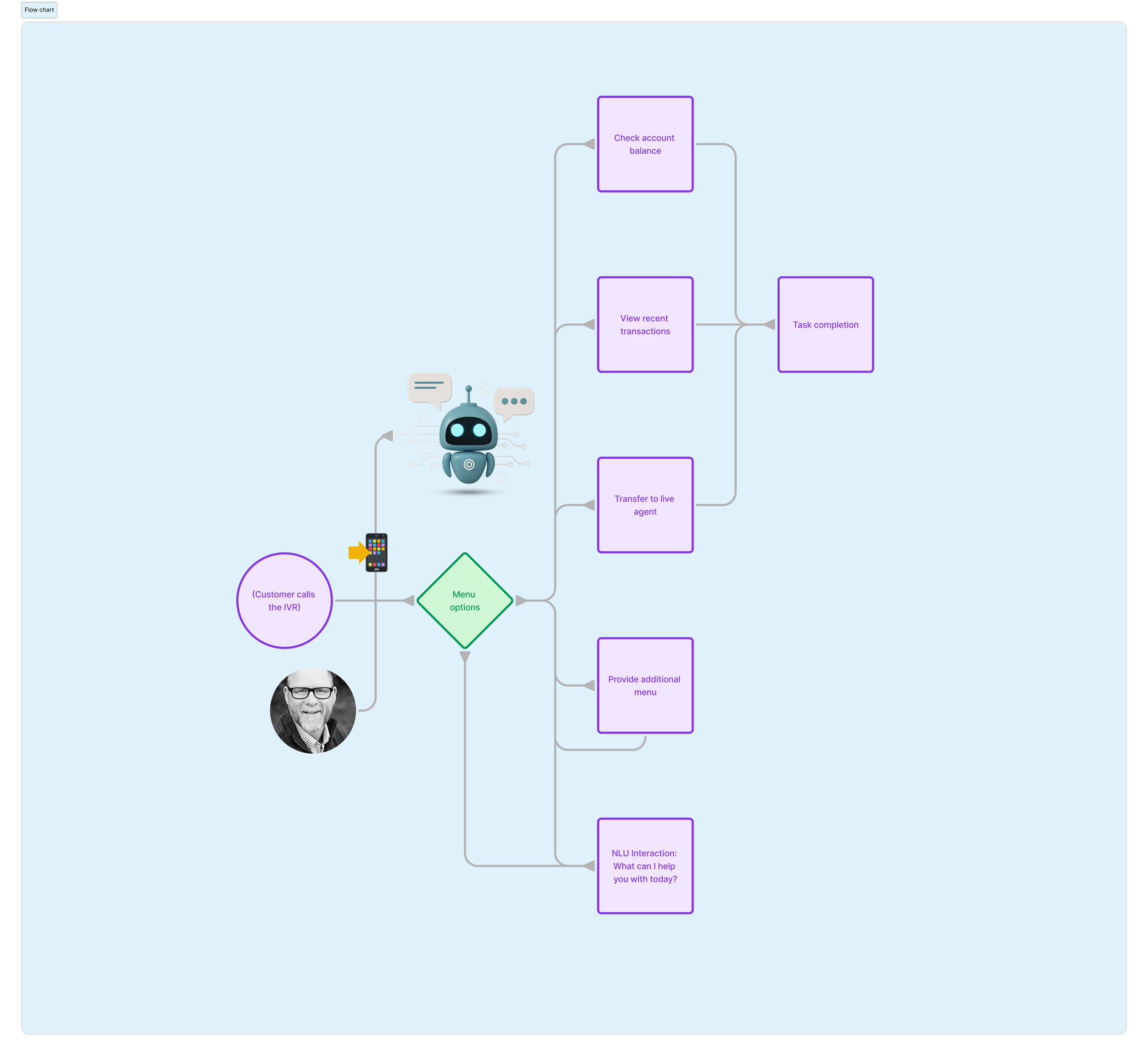
Designing the IVR Channel with Kore.ai
Setting Up the Kore.ai Platform
Account Creation: Created a Kore.ai account and set up a new project for the banking IVR.
Bot Creation: Initialized a new virtual assistant (bot) specifically for banking services.
Channel Integration: Configured the bot to work as an IVR by integrating it with the bank’s telephony system.
Defining Intents and Dialog Flows
Intent Identification:
Identified key intents based on customer needs (e.g., “Check Account Balance,” “Open New Account,” “Transfer Funds”).
Used Kore.ai’s Natural Language Understanding (NLU) engine to train the bot on these intents.
Dialog Flow Design:
Designed conversational flows for each intent using Kore.ai’s Dialog Builder.
Example: For “Check Account Balance,” the flow included:
Prompt: “Would you like to check your savings or checking account balance?”
User Input: “Savings.”
Response: “Your savings account balance is $X.”
Context Management:
Enabled context retention to allow follow-up questions (e.g., “What’s my checking account balance?” after checking savings).
Step 4: Testing – Validating the Design
Objective
To test the IVR with real users and identify areas for improvement.
Methods
Usability Testing: Conducted remote usability tests with 20 participants.
A/B Testing: Tested different versions of the conversational flow to determine which performed better.
Feedback Collection: Gathered feedback from participants on their experience.
Key Insights
Users appreciated the natural language capabilities but wanted faster response times.
Some users struggled with more complex tasks like opening a new account.
Personalization was well-received but needed to be more consistent.
Visual: Usability Testing Session
Step 5: Iteration – Improving the Design
Objective
To refine the IVR based on user feedback and testing results.
Changes Implemented
Optimized Response Times: Improved the backend integration to reduce latency.
Simplified Complex Flows: Broke down complex tasks into smaller, more manageable steps.
Enhanced Personalization: Integrated more customer data to provide tailored responses.
Step 6: Deployment and Results
Objective
To launch the IVR and measure its impact on customer satisfaction and operational efficiency.
Results
Customer Satisfaction: Increased by 25% based on post-call surveys.
Call Deflection: Reduced live agent calls by 30% for simple tasks like checking account balances.
Task Completion Rate: Improved by 40% for tasks like opening new accounts.
Step 7: Learnings and Future Improvements
What I Learned
User Feedback is Crucial: Continuous feedback loops are essential for refining conversational designs.
Balance Simplicity and Functionality: While simplicity is key, the IVR must also handle complex tasks effectively.
Personalization Drives Engagement: Customers respond positively to personalized experiences.
Future Improvements
Voice Biometrics: Integrate voice recognition for added security and personalization.
Proactive Assistance: Use AI to predict customer needs and offer assistance before they ask.
Omnichannel Consistency: Ensure the IVR experience is consistent across all customer touchpoints.
Conclusion
Designing an intelligent IVR with Kore.ai was a rewarding challenge that required a deep understanding of customer needs, thoughtful design, and continuous iteration. By following the human-centered design approach, we were able to create a solution that not only met but exceeded customer expectations. This project reinforced the importance of empathy, collaboration, and innovation in creating conversational experiences that truly make a difference.
Project Overview
Working with a mid-sized regional bank serving 2 million customers, we implemented a IVR Interactive Voice Response banking assistant using Kore.ai to address increasing customer service demands and reduce operational costs. The solution achieved a 45% reduction in call center volume and 92% customer satisfaction within six months of deployment.